Before you build: A look at AI agentic systems with Red Hat AI
The technical evolution to agentic AI
Agentic AI is reshaping how enterprises think about automation, decision making, and scalability. But building a real-world agent is not as simple as prompting a chatbot. Production-ready agentic systems require more than language models: they demand a unified architecture that coordinates reasoning, orchestrates tools, maintains memory, safeguards data, and governs behavior.
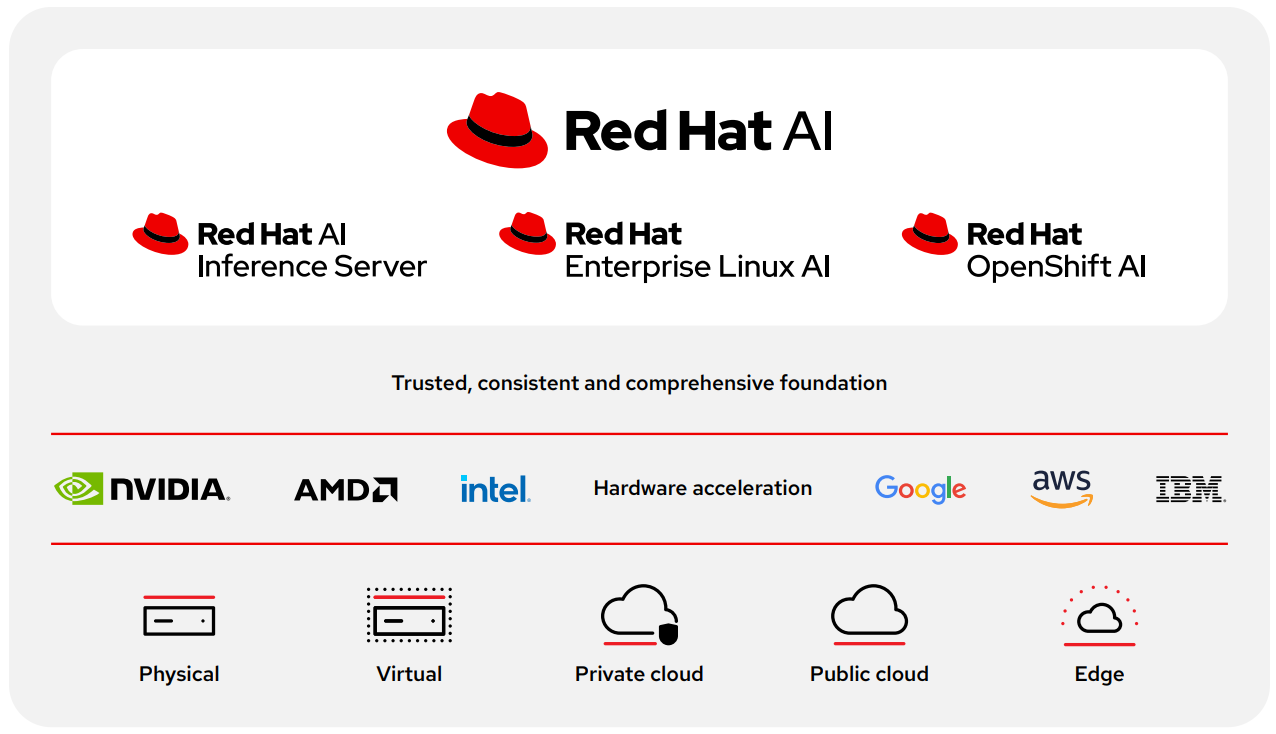
This e-book takes a technical look at that architecture, grounded in Red Hat’s open source approach. From inference and tool orchestration to safety and observability, each building block must be modular, security focused, and ready for production. That’s where Red Hat® AI comes in. Built with Red Hat OpenShift® AI and powered by Llama Stack, Red Hat AI is a platform that provides the scaffolding to construct, deploy, and manage intelligent agents at scale.
Rather than navigating fragmented frameworks and inconsistent toolchains, organizations can use Red Hat AI to standardize how they build and scale agentic workflows. Through open standards such as the Model Context Protocol (MCP), Red Hat helps unify how agents discover and use tools. By integrating safety, evaluation, and infrastructure automation, Red Hat helps teams go from proof-of-concept to production with greater repeatability and trust.
This is the next stage in enterprise AI, and standardization is the foundation that makes it possible.
Terms to know
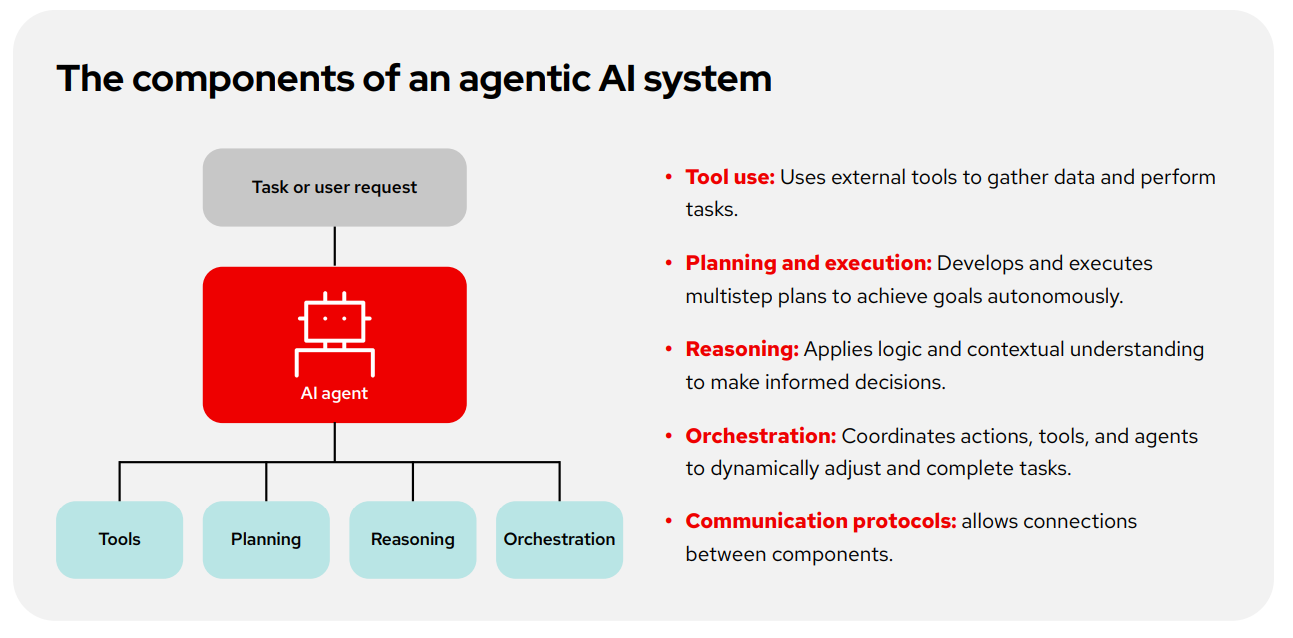
- Agentic AI systems and workflows.
Agentic AI systems are more than just large language models (LLMs). They’re a collection of multiple AI systems that work together to use reasoning, memory, planning, and outside tools to carry out complex tasks over time. These systems follow structured workflows, allowing an AI to act autonomously or semi-autonomously in response to real-world conditions. - The Model Context Protocol (MCP).
MCP is an open standard that defines how AI agents interact with tools, data, and memory in a consistent, interpretable way. It helps developers design AI systems that are modular, reusable, and easier to debug or scale. - Llama Stack.
The Llama Stack is a unified software layer that wraps Llama models in production-ready tools, including application programming interfaces (APIs), orchestration, logging, and tool integration. It simplifies the deployment and operation of Llama-based agentic AI systems in enterprise environments. - LangChain.
LangChain is an open source framework that helps developers build complex applications using language models. Much like MCP and Llama Stack, it provides tools to connect models with external data, memory, and tools. While it is not the baseline framework used with Red Hat AI, Red Hat AI is a flexible open platform that can support other approaches if they are appropriate for a project.
Chapter 1: Create and deploy AI agents with Red Hat AI
Creating an agentic AI system goes well beyond embedding a large language model (LLM) into an application. At the core of any effective agent is a system that can reason, plan, act, and learn, and all of that relies on a diverse set of technical components. These include reasoning chains that divide problems into sub-tasks, prompts that define agent behavior, memory for maintaining context, and external tools that provide the ability to take action beyond the LLM’s pretrained weights.
Red Hat AI helps streamline this complex architecture. Built with OpenShift AI as a core component, the platform brings together essential capabilities such as inference, orchestration, security, observability, and compliance, and connects them to the tools AI agents need to function effectively.
With Red Hat AI, teams can begin with manageable use cases and scale over time. Many organizations start by building internal retrieval agents, deploying LLM-enhanced knowledge bots that answer questions based on company-specific data. Others build agents for log remediation and IT incident resolution, integrating Red Hat OpenShift observability with Red Hat Ansible® Automation Platform and external application programming interfaces (APIs). Another common scenario is AI-assisted code migration, where agents support traditional-to-modern transitions by analyzing repositories and proposing upgrade paths.
Crucially, these agents are not just single-shot assistants, but part of multistep workflows with embedded reasoning and memory. As complexity increases, Red Hat offers comprehensive lifecycle management and orchestration capabilities for multiagent applications with clear delegation and decision checkpoints.
The path to enterprise-scale agentic AI starts with this foundation: composable architecture, repeatable tooling, and a unified platform that turns experimentation into operations. Red Hat AI helps teams to build with confidence, and deploy with intent.
Use cases
How organizations are building agents today
Customer support at scale
A cybersecurity company implemented an AI-powered support system to automate live chat and ticket resolution, aiming to cut wait times and reduce the burden on human agents. An intake agent processes the query, which then goes to a classification agent that performs sentiment tagging, urgency analysis, and profanity checks using keyword lists and gen AI sentiment analysis. Problematic language triggers a manual review.
Next, a resolution agent generates responses using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), drawing from internal docs and past tickets. If needed, a routing agent escalates unresolved or low-confidence tickets to a human support representative. Human agents validate AI-suggested replies, especially for compliance-sensitive content. Airtable logs track overrides and errors, supporting ongoing model improvement. After closure, sentiment is reevaluated to confirm customer satisfaction.
Chapter 2: Red Hat OpenShift AI: The enterprise-scale platform for the AI lifecycle
Transitioning from prototype to production remains among the most persistent challenges in enterprise AI, especially with agentic applications. OpenShift AI helps organizations build, run, and manage agentic applications.
OpenShift AI incorporates core Red Hat technologies to provide a production-grade foundation for agentic workloads. Central to this is its operator-based model, which encodes deployment best practices and automates platform configuration. Operators streamline everything from autoscaling and observability integration to performance tuning and horizontal or vertical scaling strategies—freeing engineering teams to focus on building agents, not managing infrastructure.
OpenShift AI builds on the capabilities of Red Hat OpenShift to provide a platform for managing the lifecycle of generative and predictive AI models at scale.
The platform’s native integration with components like Llama Stack and MCP helps unify development and deployment practices. Developers can build on top of Llama Stack’s OpenAI-compatible API and deploy agents with confidence, knowing the same interfaces used in local testing are supported in production environments. MCP servers provide a standard way to expose and manage tools, with compatibility across frameworks and robust integration into Red Hat’s security and observability stack.
Security and compliance are integral to OpenShift AI. Red Hat’s longstanding focus on regulated environments means agentic applications can be deployed with guardrails and role-based access already built in. Integrated observability tooling helps teams trace agent decisions, monitor tool invocations, and build analytics pipelines that support ongoing evaluation.
The result is a unified platform where AI engineers, IT teams, and security stakeholders can collaborate more effectively. Whether deploying a simple support agent or a multiagent orchestration pattern for internal automation, OpenShift AI helps operationalize agentic AI systems— safely, repeatedly, and at scale.
Use case
How organizations are building agents today
AI-focused business process automation
A customer developed a procurement assistant that could navigate enterprise resource planning (ERP) APIs via MCP, interpret policy documents, and recommend vendor approvals. This agent automated routine steps such as verifying supplier eligibility and reviewing contract terms, reducing bottlenecks in procurement workflows while maintaining compliance. It serves as a model for embedding agentic workflows into existing enterprise systems without the need to rebuild core logic.
Chapter 3: The Model Context Protocol: Standardizing agent-tool interaction
Modern agentic systems rely on tool use to extend the capabilities of LLMs. While LLMs provide reasoning, they need tools to take action, access enterprise systems, and gather real-time information. MCP provides the missing connective tissue between agents and these external tools. While MCP was only recently introduced, it has rapidly been adopted as a new standard for agentic AI.
Before MCP, tool integration was manual, inconsistent, and difficult to scale. Developers had to write custom code to define how agents discover and interact with APIs. This created duplication across teams, made updates less stable, and introduced risk every time a system changed. MCP standardizes this process with a modular, interoperable specification that allows agents to discover, select, and invoke tools reliably, much like a USB-C standard for AI workflows.
With MCP, developers expose functionality as tools using a common protocol. These tools can span APIs, databases, business systems, or even internal utilities. MCP servers act as a hub where tools are hosted, documented, and secured. Agents can then dynamically query this server, reason about tool usage, and invoke workflows across multiple systems.
This standardization opens the door to broader participation. With an MCP-based architecture, teams can reuse existing tool definitions, accelerate onboarding, and reduce platform fragmentation. For smaller or larger LLMs, MCP also helps organizations have more consistent tool usage without retraining models or rewriting logic.
However, MCP is not without its challenges. Poorly written tool descriptions can confuse agents, leading to misfires or hallucinated behavior. Worse, tools that expose insecure prompt strings or overly broad permissions risk becoming vectors for exploitation.
Red Hat has a roadmap toward a MCP gateway that helps mitigate these risks by embedding governance, security considerations, and observability directly into the MCP server architecture. When MCP servers are deployed within OpenShift AI, they inherit native integration with Red Hat’s platform-level policy enforcement, role-based access controls, and audit mechanisms. This means access to tools exposed through MCP can be strictly managed by role and namespace, aligning with identity and authorization policies.
Additionally, the tool descriptions and prompt schemas hosted within MCP can be automatically scanned for vulnerabilities using the container and application security toolchain from Red Hat OpenShift. This allows platform teams to identify potentially dangerous tool configurations, such as tools that allow prompt injection or that expose sensitive backend systems without proper input validation.
From an operational perspective, Red Hat OpenShift observability tools allow continuous monitoring of agent-tool interactions. Teams can view tool invocation patterns, track usage metrics, and set alerts for anomalous behavior. Integrated audit logs provide traceability across tool usage and decision-making chains, helping enterprises meet internal and external compliance requirements.
Use case
How organizations are building agents today
Customer support at scale
A cybersecurity company implemented an AI-powered support system to automate live chat and ticket resolution, aiming to cut wait times and reduce the burden on human agents. An intake agent processes the query, which then goes to a classification agent that performs sentiment tagging, urgency analysis, and profanity checks using keyword lists and gen AI sentiment analysis. Problematic language triggers a manual review.
Next, a resolution agent generates responses using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), drawing from internal docs and past tickets. If needed, a routing agent escalates unresolved or low-confidence tickets to a human support representative. Human agents validate AI-suggested replies, especially for compliance-sensitive content. Airtable logs track overrides and errors, supporting ongoing model improvement. After closure, sentiment is re-evaluated to confirm customer satisfaction.
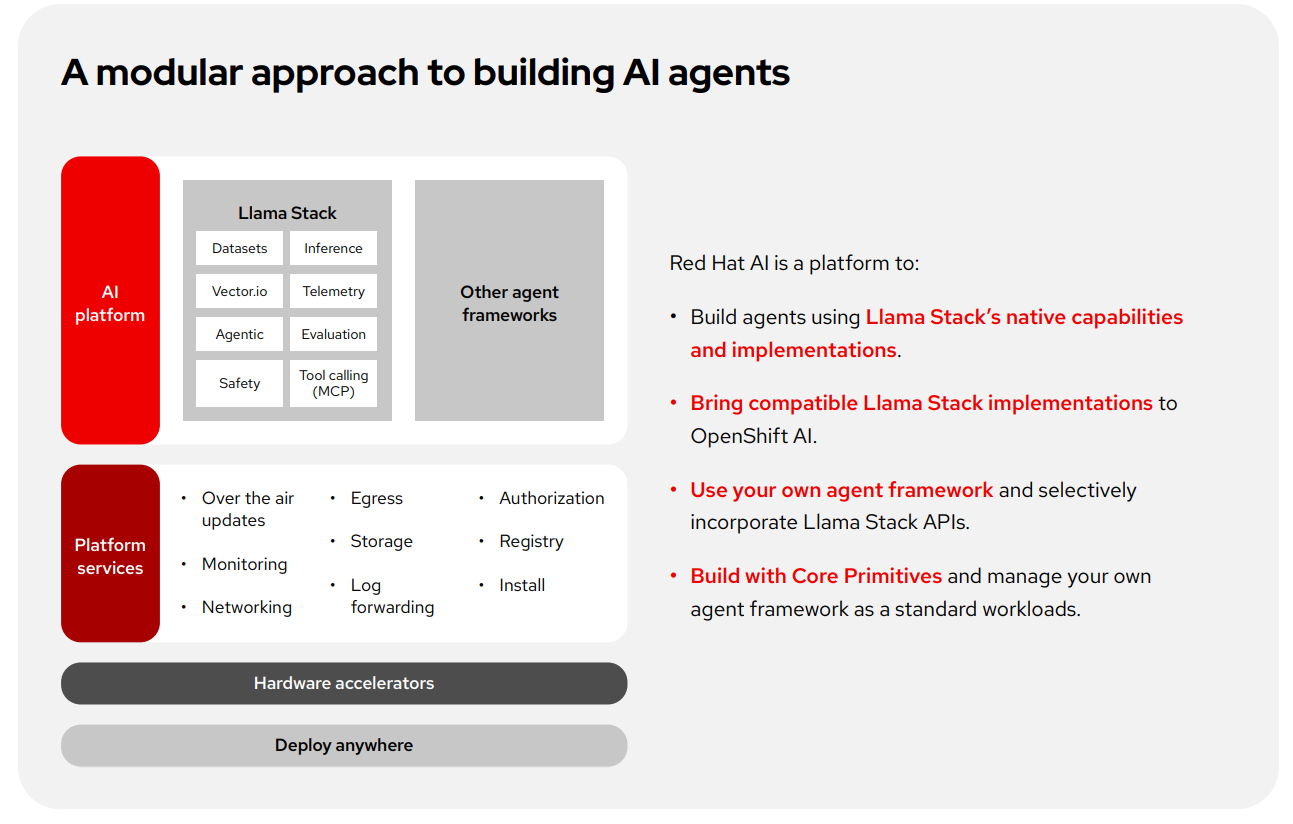
Chapter 4: Llama Stack: The unified AI API server with OpenShift AI
Llama Stack is Red Hat’s unified AI control plane, an OpenAI-compatible API server built to streamline the development, deployment, and management of agentic AI applications. Acting as a central interface for inferencing, memory, tool orchestration, and evaluation, Llama Stack provides developers with the consistency and flexibility needed to build sophisticated agents across environments.
Unlike many other solutions, which are typically hosted services, Llama Stack helps organizations produce a hosted-style experience on owned hardware or clusters. For organizations that need data sovereignty, have specific infrastructure requirements, or want to avoid being tied to a specific vendor, this flexibility is essential.
At its core, Llama Stack delivers a standard API layer that supports the full agentic lifecycle including compatibility with OpenAI APIs beyond just inference. It integrates directly with OpenShift AI and supports common agent tasks such as retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), safety, evaluation, telemetry, and context-aware inferencing. Developers can start with a lightweight local deployment and scale to enterprise-grade infrastructure, using the same APIs, libraries, and interfaces throughout.
Llama Stack is API-compatible with OpenAI's tool-use interfaces and works with many well-known and popular frameworks. This allows teams to integrate existing agents and workflows without rearchitecting, while still benefiting from a consistent interface and lifecycle management tools across environments.
What distinguishes Llama Stack is its open-source API layer and server that standardize AI application development across providers. It supports OpenAI-compatible inference alongside additional APIs for other AI functions, such as evaluations, post-training, and vector stores, and shields to power RAG and agent workflows. Llama Stack can run in self-hosted environments, on-premise, or in the cloud, giving organizations deployment flexibility.
Within OpenShift AI, a Kubernetes Operator manages Llama Stack lifecycle tasks such as autoscaling, observability, and access control, giving developers and platform teams a unified set of tools for scaling agents reliably. Llama Stack also includes native support for evaluation and telemetry, including OpenTelemetry, to help teams validate AI system performance, monitor safety metrics, and trace agent behavior across production environments.
Beyond just inferencing, Llama Stack is designed to support the many moving parts of agentic systems. It can serve as a bridge between hosted and local models, standardize access to safety tools such as TrustyAI, and facilitate interaction with MCP servers. Developers get a consistent platform for testing, iterating, and operationalizing agents, whether they're running proof-of-concept demos or automating production IT workflows.
Llama Stack turns the complexity of agent orchestration into a modular, repeatable process. With Red Hat’s support, and integration with OpenShift AI, it gives teams the control plane they need to scale agentic AI systems safely and predictably.
Use case
How organizations are building agents today
Developer productivity
A software organization built a code migration assistant that analyzed traditional Java applications and recommended updates to align with modern frameworks. The agent used Llama Stack for inference and MCP-integrated tools to validate compatibility and suggest upgrade paths. This streamlined the migration process, reducing technical debt and improving application resilience. It also helped development teams focus on feature innovation rather than spending time rewriting legacy code.
Conclusion: Red Hat AI: Your technical foundation for agentic AI success
Agentic AI promises more intelligent, adaptive applications, but without standardization, enterprise teams risk fragmentation, inefficiency, and operational risk. Red Hat AI provides the scaffolding needed to build these systems with confidence. Through components like OpenShift AI, MCP, and Llama Stack, Red Hat offers a consistent foundation to take AI agents from proof-of-concept to production.
By integrating reasoning, tool use, memory, safety, and evaluation into a unified platform, Red Hat AI simplifies how teams experiment, scale, and operationalize AI agents.
- Developers gain access to production-grade APIs.
- Platform teams can manage lifecycles and enforce security.
- Organizations benefit from open standards that protect their investments.
Whether deploying a simple internal bot or architecting multiagent systems, Red Hat AI equips you with what you need to build security-focused, enterprise-grade agentic applications—repeatably, and on your terms.